Calcined Alumina Polishing: Precision Surface Finishing for Metals, Ceramics & Glass
Date: May-15-2025 Categories: News、Alumina、Aluminium Hydroxide Views: 525
Calcined alumina polishing is a dependable, high-purity solution for precision surface finishing. It delivers consistent cut, clean scratch patterns, and bright surfaces on stainless steel, superalloys, ceramics, and glass. If you are seeking a Manufacturer, Supplier, or Factory in China for stable Wholesale supply, Banlan Chem provides engineered grades of calcined alumina polishing powders for repeatable quality and cost efficiency. This guide explains how Calcined Alumina Polishing works, where it fits in your process, and how to specify the right grade for your line.

Contents
- What Is Calcined Alumina Polishing?
- Why Choose Calcined Alumina vs Other Abrasives
- Key Applications: Metals, Ceramics & Glass
- Polishing Mechanism & Surface Science
- How to Select Grades & Grit Sizes
- Slurry Preparation & Process Parameters
- Typical Process Flows by Substrate
- Quality Control, Testing & Metrology
- Troubleshooting & Defect Prevention
- Safety, Handling & Environmental Notes
- OEM/ODM Support & Wholesale Supply in China
- Reference Specifications for Calcined Alumina Polishing
- FAQ: Calcined Alumina Polishing
- Related Products & Internal Links
- Contact Banlan Chem
1) What Is Calcined Alumina Polishing?
Calcined Alumina Polishing uses high-purity α-Al2O3 powder that has been thermally treated (calcined) to stabilize crystal phase, hardness, and particle integrity. Controlled particle size distribution and low soda content help deliver uniform removal rates and low surface roughness (Ra/Rq). Because calcined alumina is tough yet clean-cutting, it balances stock removal and final gloss across lapping, pre-polish, and final polish steps.
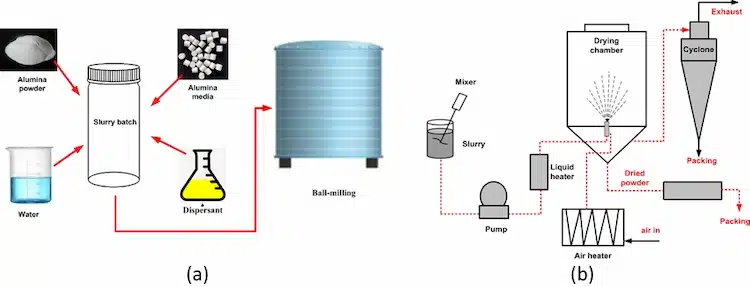
2) Why Choose Calcined Alumina vs Other Abrasives
- Consistency: Stable α-phase reduces variability in removal rate and scratch depth.
- Clean finish: Tight particle classification lowers rogue particles and stray scratches.
- Chemical inertness: Compatible with many coolants and pH windows; won’t corrode metals.
- Cost-effective: Compared with diamond, Calcined Alumina Polishing can cut costs for large surfaces and general precision finishing.
- Versatility: Works on stainless steel, tool steel, Ti alloys, alumina ceramics, zirconia, and glass.
For more information on alumina polishing mechanisms, see the Buehler TECHNotes – “How to Select and Use Final Polishing Oxide Media” , which discusses the use of alumina abrasives in precision polishing. :contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
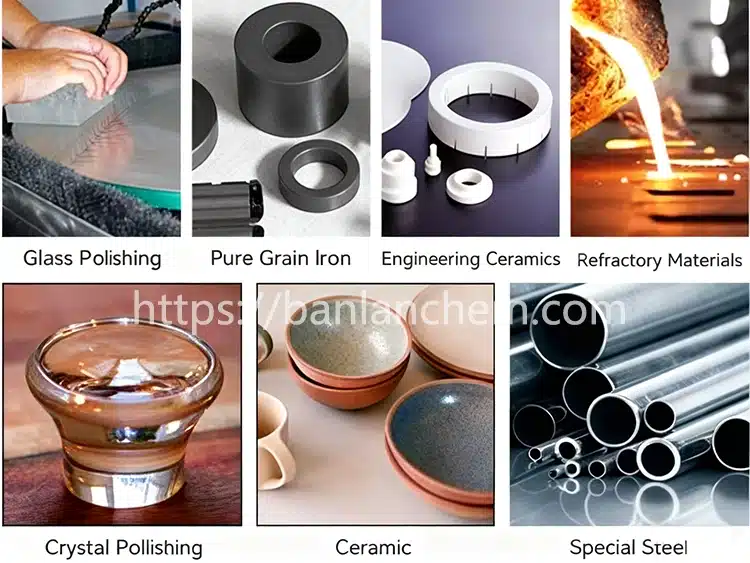
3) Key Applications: Metals, Ceramics & Glass
Calcined Alumina Polishing supports multi-industry finishing lines:
- Metals: Stainless steel sheets, castings, pump components, medical instruments, watch cases.
- Ceramics: Alumina substrates, zirconia parts, mechanical seals, ceramic bearings.
- Glass: Optical glass, display glass edges, molded glass, laboratory glassware.
- Alloys: Nickel-based and titanium components in aerospace and energy sectors.

4) Polishing Mechanism & Surface Science
In Calcined Alumina Polishing, particles micro-cut asperities while rolling or sliding under controlled pressure. The α-alumina crystal’s hardness produces predictable micro-grooves that quickly convert to a uniform matte and then to a gloss during finer steps. Low contaminant content minimizes embedded debris and discoloration. A clean fluid system prevents agglomeration and maintains dispersion stability for smoother surface energy and wetting.
5) How to Select Grades & Grit Sizes
Match particle size to your target Ra and material hardness. Use coarser grades for bulk removal and finer grades for final gloss. The table shows typical guidance:
| Stage | Target Ra (µm) | Typical D50 (µm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lapping / Pre-polish | 0.2–0.5 | 3–5 | High removal rate on metal plates and ceramic flats. |
| Intermediate polish | 0.05–0.2 | 1–3 | Balances cut and surface refinement. |
| Final polish | <0.05 | 0.3–1.0 | Low scratch count, bright mirror finish on glass/ceramics. |
If your process requires enhanced purity or specific rheology, request OEM/ODM customization from a Manufacturer and Supplier in China with strong classification, surface modification, and sintering control. Banlan Chem can tailor Calcined Alumina Polishing for Wholesale programs.
For best polishing results with premium grades, you can consult the detailed specifications, or choose a calcined alumina polishing grade from our factory that matches your surface finish requirements.
6) Slurry Preparation & Process Parameters
Dispersion: Pre-wet powder with DI water. Mix at moderate shear. Avoid air entrainment.
Solids loading: 5–30 wt% depending on pad, pressure, and target throughput.
pH control: Slightly acidic to neutral for metals. Neutral to slightly basic for ceramics and glass. Verify compatibility with substrates and pads.
Additives: Dispersants to stabilize particles. Rust inhibitors for steel. Biocides for long-life tanks.
Filtration: Side-stream filtration at 1–5 µm to remove swarf and large agglomerates.
Flow rate: Maintain fresh slurry at the pad–part interface to keep removal rate stable.
Pressure & speed: Start low. Increase stepwise while monitoring temperature, RR (removal rate), and scratch counts.
7) Typical Process Flows by Substrate
7.1 Stainless Steel & Superalloys
- Pre-lap with 3–5 µm calcined alumina slurry on hard plate.
- Intermediate polish with 1–3 µm on resilient pad.
- Final polish with 0.5–1.0 µm. Flush and passivate as required.

7.2 Alumina & Zirconia Ceramics
- Plane with 5 µm on composite plate to remove green machining marks.
- Refine with 1–3 µm to reach Ra 0.1–0.2 µm.
- Finish with 0.3–1.0 µm for mirror surface and tight flatness.

7.3 Glass & Optical Components
- Pre-polish edges with 3 µm slurry to remove chips.
- Intermediate polish with 1 µm on felt or polyurethane pad.
- Final polish with sub-micron calcined alumina for high gloss and low haze.
If you need stable industrial supply and reliable performance, visit our industrial calcined alumina for polishing & supply page for wholesale grades and factory support.
8) Quality Control, Testing & Metrology
- Particle size: Laser diffraction/DLS to verify D50 and tails.
- Purity: ICP/EDX for Na2O and trace metals that affect corrosion or color.
- PSD width: Narrow PSD = fewer deep scratches and more uniform Ra.
- Surface metrics: Ra, Rq, Rz with calibrated stylus or optical profilometer.
- Defect audit: Microscope/SEM images for pits, pull-outs, embedded debris.
- Bath control: pH, conductivity, viscosity, and bacteria counts for recirculating systems.
Industry standards such as ASTM E407 – Standard Practice for Microetching Metals and Alloys provide valuable references for evaluating polished surfaces and verifying consistency.
9) Troubleshooting & Defect Prevention
Random scratches: Check filtration, tank cleanliness, and rogue particles. Consider a tighter PSD grade.
Haze or low gloss: Reduce pressure. Increase pad conditioning. Switch to finer Calcined Alumina Polishing grade.
Slow removal rate: Raise solids loading or platen speed gradually. Verify pad life. Check slurry pH.
Orange peel on metals: Lower pressure and temperature. Improve coolant flow. Step down grit sizes more gradually.
Corrosion stains: Add inhibitors. Shorten dwell time. Rinse and dry promptly after polish.
10) Safety, Handling & Environmental Notes
- Use dust control when handling dry powders.
- Wear goggles, gloves, and appropriate respirators when necessary.
- Label storage bins. Keep materials dry. Follow local disposal regulations for spent slurry and swarf.
11) OEM/ODM Support & Wholesale Supply in China
As a Manufacturer and Wholesale Supplier in China, Banlan Chem supports OEM/ODM programs for Calcined Alumina Polishing. We help you match powder grade to pad, platen, and coolant. We also assist in scale-up, cost modeling, and packaging options for Factory lines that run 24/7. Stable supply, consistent PSD, and technical documents are included to reduce qualification time.

12) Reference Specifications for Calcined Alumina Polishing
- Chemical: Al2O3 ≥ 99.5% typical; Na2O low.
- Phase: α-alumina after controlled calcination.
- PSD Options (D50): 0.3 µm, 0.5 µm, 1 µm, 3 µm, 5 µm (custom on request).
- Moisture: Low moisture, flowable powder; slurry grades available.
- Packaging: 10–25 kg bags; 500–1000 kg big bags; OEM lab packs for trials.
13) FAQ: Calcined Alumina Polishing
Q1. Is calcined alumina suitable for both cutting and final finishing?
Yes. Coarser grades handle quick stock removal. Finer grades produce low Ra finishes. That is why Calcined Alumina Polishing is common from pre-polish to mirror-finish stages.
Q2. How does it compare to diamond?
Diamond cuts faster on extremely hard substrates. However, Calcined Alumina Polishing offers cleaner finishes and lower consumable cost for many metals, ceramics, and glass, especially at scale.
Q3. What pH should I run?
Start near neutral. Shift slightly acidic for metals and slightly basic for ceramics/glass as needed. Verify corrosion and pad compatibility before full-scale runs.
Q4. Can Banlan Chem provide custom PSD or functionalized surfaces?
Yes. As a Manufacturer and Supplier in China, we offer OEM/ODM customization, including tighter PSD, surface treatment, and slurry concentrates for Wholesale orders.
Q5. How do I minimize random scratches?
Tighten filtration, improve housekeeping, and choose a narrower PSD calcined alumina grade. Condition pads regularly. Validate each incoming lot with a micro-scratch audit.
14) Related Products & Internal Links
- Calcined Alumina Powder – Manufacturer & Wholesale Supplier
- Tabular Alumina – High-Purity Sintered α-Al2O3
- Alumina Powder – Fine Grades for Polishing & Ceramics
- Activated γ-Al2O3 Powder – Adsorbent & Catalyst Carrier
- White Fused Alumina – Abrasive for High-Cut Applications

15) Contact Banlan Chem
Looking to qualify Calcined Alumina Polishing for a new line or transfer an existing spec? Contact Banlan Chem for grade recommendations, trial samples, and Wholesale pricing from our Factory in China. We support Manufacturer and Supplier partners worldwide with OEM/ODM customization, documentation, and logistics.
Calcined Alumina Polishing delivers stable removal rates, low scratch counts, and bright finishes across metals, ceramics, and glass. Choose a trusted Manufacturer, Supplier, and Factory in China to secure Wholesale supply, technical support, and consistent quality for your precision finishing workflow.














