What Is Tabular Alumina? Properties, Melting Point, and Applications

Tabular alumina is a high-quality α-Al₂O₃ material. It has a flat, plate-like alumina crystal structure. It is produced by top-grade calcined aluminium oxide. Banlanchem is a trusted manufacturer, supplier, and factory of tabular alumina and related products.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Tabular Alumina
- Key Features
- Production Methods
- Physical and Chemical Properties
- Applications
- Tabular Alumina vs Aluminum
- FAQ
- Contact Banlanchem
Introduction to Tabular Alumina
Tabular alumina is a high-performance alumina mineral. It combines micron and nano powders. It offers high hardness, thermal stability, and smooth surface. Its high purity and strong surface activity make it ideal for various industries.
As a wholesale material, tabular alumina is used in ceramics, abrasives, pigments, and coatings. The alumina melting point is around 2050°C (3722°F). This ensures it works under high heat without melting or breaking. Its thermal stability is much higher than aluminum.
Banlanchem, a leading manufacturer and supplier, provides consistent, high-quality tabular alumina for industrial use. Our factory ensures reliable supply for wholesale and bulk orders.
Key Features of Tabular Alumina
- High hardness and thermal stability
- Good dispersibility in water and solvents
- Smooth surface and high purity
- Strong surface activity and barrier effect
- Excellent reflectivity and adhesion
- Long-lasting and safe for cosmetics
Production Methods
1. Hydrothermal Method
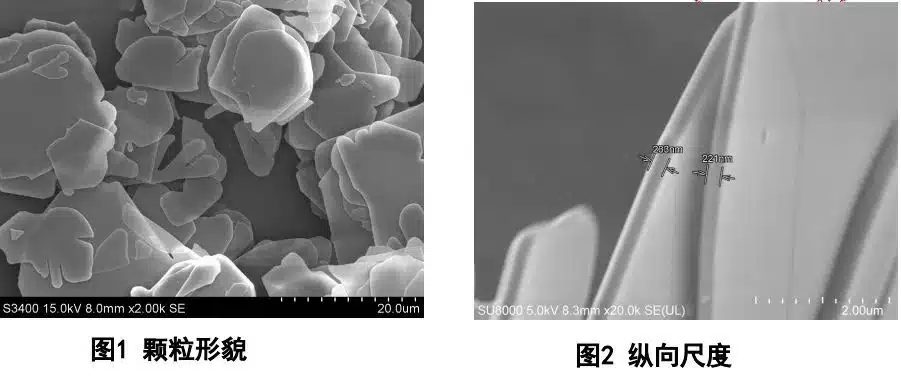
High-pressure vessels create crystals under heat. Produces thin, pure alumina plates. Energy consumption is high and cycle time is long. Suitable for special industrial applications. The method ensures precise alumina crystal structure.
2. Molten Salt Method
Alumina is combined with molten salts at high temperatures. Atomic-level rearrangement occurs. Produces high-quality calcined aluminium oxide. Crystal growth is fast and efficient. Widely used by factories and suppliers for large-scale wholesale production.
3. Sol–Gel Method
Forms a precursor via hydrolysis and condensation. Then calcined into α-Al₂O₃. Equipment-friendly and low-cost. Good for manufacturer scale production. Controls particle size and morphology precisely.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Alumina melting point: ~2050°C (3722°F)
- Alumina melting temperature is stable for high heat applications
- High thermal conductivity
- Chemical resistance to acids and alkalis
- Plate-like alumina crystal structure
These properties make tabular alumina much harder and more heat-resistant than aluminum. This is key for industrial materials requiring extreme thermal endurance. Alumina vs aluminum is a common comparison for engineers.
Applications of Tabular Alumina
1. Polishing and Abrasives
- Better polishing performance than conventional abrasives
- Less scratching on metals, semiconductors, and gemstones
- High hardness ensures consistent quality

2. Pearlescent Pigments
- Provides bright colors and high reflectivity
- Used in cosmetics, coatings, and decorative finishes
- Safer and purer than mica-based pigments

3. Inorganic Fillers
- Enhances strength and crack resistance in ceramics and plastics
- Improves thermal conductivity of composites
- Widely used in electronics and industrial materials
4. Cosmetics
- Used in powders and creams
- Improves smoothness, adhesion, and wear-resistance
- Safe for sensitive skin products
5. Functional Coatings
- Anti-radar, UV-blocking, and photocatalytic coatings
- Applied in solar panels and electronic devices
- High chemical stability and long-term performance
For more detailed industrial applications, see our Alumina Market Report and Top Alumina Producers 2024.
Tabular Alumina vs Aluminum
| Feature | Tabular Alumina | Aluminum Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic oxide | Metal |
| Hardness | High (Mohs ~9) | Low (Mohs ~2.5) |
| Thermal Stability | ~2050°C | ~660°C |
| Electrical Conductivity | Insulator | Conductor |
| Applications | Ceramics, abrasives, coatings, pigments | Construction, packaging, electrical |
FAQ about Tabular Alumina
- Q1: What is the melting point of tabular alumina?
A: ~2050°C (3722°F). Ensures high thermal stability. - Q2: How is tabular alumina made?
A: Hydrothermal, molten salt, or sol–gel methods. Produces high-quality α-Al₂O₃. - Q3: Is tabular alumina the same as aluminum?
A: No, tabular alumina is a ceramic oxide. Much harder and heat-resistant. - Q4: What are the main applications?
A: Polishing, pigments, fillers, cosmetics, coatings, electronics. - Q5: Where can I buy tabular alumina?
A: From Banlanchem manufacturer, supplier, and factory. Alumina Powder available for wholesale.
Contact Banlanchem

For inquiries, please visit our official website: https://banlanchem.com. We are a professional manufacturer, supplier, and factory of tabular alumina and other calcined aluminium oxide products.














