Can Alumina Powder Be Used in High-Temperature Applications?
Can alumina powder be used in high-temperature applications? This is a common question for engineers, refractory designers, and material buyers. Alumina powder is known for its thermal stability. It is widely used in furnaces, kilns, and high-heat industrial systems.
As a professional alumina powder manufacturer and supplier, BanlanChem works with customers who require reliable materials for extreme thermal environments. This article explains how alumina powder performs at high temperatures, where it works best, and what limits apply.
Table of Contents
- What Is Alumina Powder?
- Thermal Properties of Alumina Powder
- Maximum Temperature Limits
- High-Temperature Applications
- Calcined Alumina vs Other Forms
- Material Selection Considerations
- Manufacturer and Factory Perspective
- Technical Summary
What Is Alumina Powder?
Alumina powder is aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃). It is an inorganic ceramic material. It has high melting temperature and strong chemical stability.
Alumina powder is produced from aluminum hydroxide. Different processing routes create different crystal phases. The most common industrial phase is alpha alumina.
Related product reference: Alumina Powder
Thermal Properties of Alumina Powder
Can alumina powder be used in high-temperature applications? The answer depends on its thermal properties.
- Melting point: approximately 2070°C
- Continuous service temperature: above 1600°C (depending on purity)
- Low thermal expansion
- High thermal shock resistance
- Excellent oxidation resistance
These properties allow alumina powder to remain stable under long-term heat exposure. It does not soften or decompose under typical industrial furnace conditions.
Maximum Temperature Limits
Although alumina powder has a very high melting point, real-world limits depend on application.
- Binder systems may fail before alumina itself
- Particle size affects sintering behavior
- Impurities can lower effective temperature limits
In most refractory and ceramic uses, alumina powder performs reliably between 1200°C and 1800°C.
High-Temperature Applications of Alumina Powder
Can alumina powder be used in high-temperature applications across industries? Yes. It is widely used in the following fields:

- Refractory bricks and castables
- High-temperature furnace linings
- Ceramic kiln furniture
- Thermal insulation components
- Wear-resistant parts exposed to heat
In these systems, alumina powder provides structural strength at elevated temperatures. It also improves corrosion resistance against molten metals and slags.
In industrial furnace systems, alumina powder is often used as a functional component rather than a structural material. Its role is to improve thermal stability, insulation performance, and chemical resistance under sustained heat exposure.
In steel reheating furnaces and ceramic kilns, alumina powder is commonly blended into refractory mixes. It helps increase service temperature limits and reduces deformation at elevated temperatures. This is especially important in zones exposed to continuous operation above 1,200°C.

Manufacturers typically select different alumina grades based on firing temperature and load conditions. For medium-temperature zones, fine alumina powder may be sufficient. For extreme heat areas, calcined alumina is often preferred due to its higher phase stability.
In these applications, alumina powder is valued for its predictable thermal behavior. It does not soften, melt, or release harmful gases when exposed to heat. This makes it suitable for long-term industrial use where temperature control and material reliability are critical.
For a detailed comparison of thermal performance, see calcined alumina vs alumina powder .
Calcined Alumina vs Other Forms
Not all alumina powders behave the same at high temperature.
Calcined alumina is the most common choice for thermal applications. It has stable crystal structure and low volatile content.
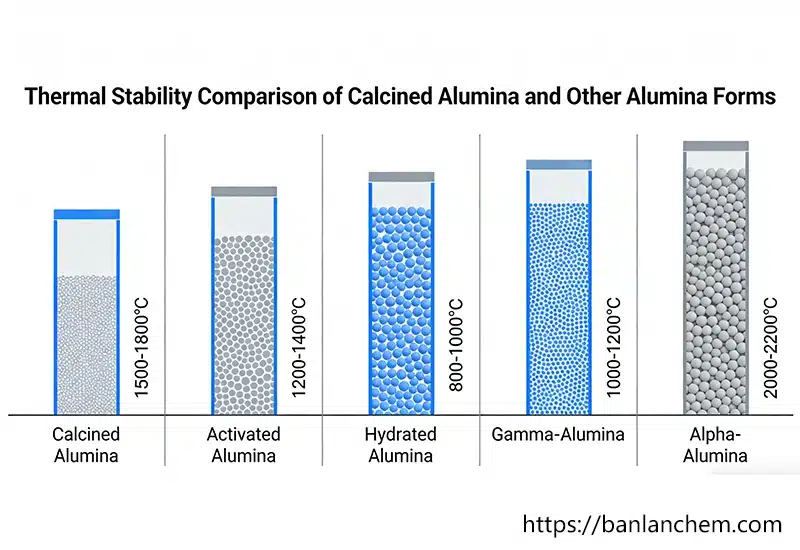
Related product: Calcined Alumina
- Hydrated alumina: lower thermal stability
- Activated alumina: high surface area, lower heat resistance
- Calcined alumina: best balance for high-temperature use
For continuous exposure to extreme heat, calcined alumina is preferred.
Material Selection Considerations
When selecting alumina powder for high-temperature applications, engineers should evaluate:
- Al₂O₃ purity level
- Particle size distribution
- Sintering temperature
- Thermal cycling conditions
- Compatibility with binders and additives
Material testing under real operating conditions is recommended. Laboratory data alone may not reflect field performance.
Manufacturer and Factory Perspective
From a manufacturer and factory perspective, alumina powder grades are designed for specific heat ranges.
Industrial buyers working with a reliable alumina powder supplier or wholesale source can select:
- Low-soda grades for refractories
- High-purity grades for advanced ceramics
- Custom particle size for controlled sintering
A qualified alumina powder manufacturer can provide technical data and batch consistency. This is critical for high-temperature systems.
FAQ About Alumina Powder at High Temperatures
Can alumina powder maintain stability under continuous high heat?
Yes. Alumina powder remains chemically stable under continuous high-temperature conditions. It does not burn or decompose during normal industrial use. However, its performance depends on particle size, purity, and processing method.
Can alumina powder maintain stability under continuous high heat?
Yes. Alumina powder remains chemically stable under continuous high-temperature conditions. It does not burn or decompose during normal industrial use. However, its performance depends on particle size, purity, and processing method.
While alumina powder is suitable for high-temperature applications, safe handling remains essential. Dust exposure and workplace controls are discussed in Is Alumina Powder Safe for Industrial Use?.
Technical Summary
Can alumina powder be used in high-temperature applications? Yes. Alumina powder is one of the most reliable ceramic materials for extreme heat.
Its high melting point, thermal stability, and chemical resistance make it suitable for furnaces, refractories, and ceramic systems. Proper grade selection is essential.
For industrial users, working with an experienced alumina powder supplier ensures stable performance and long service life in high-temperature environments.














